Blog
What is Nail Intramedullari and How is it Used in Surgery?
nail intramedullari is a crucial technique in orthopedic surgery. It involves inserting a metal rod into the medullary cavity of bones. This method stabilizes fractures and promotes healing. Surgeons often use it for long bones like the femur or tibia.
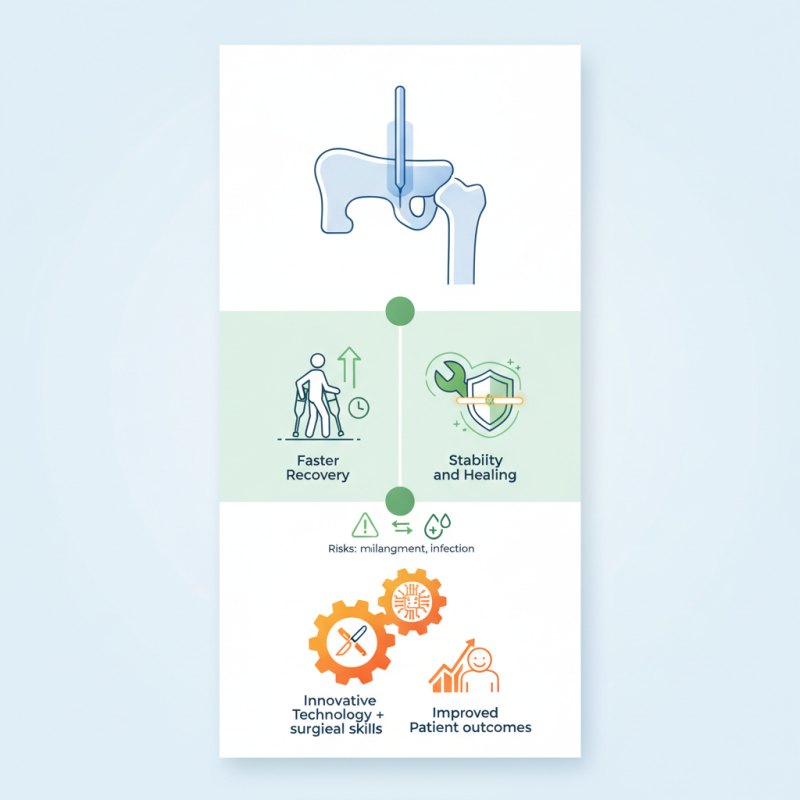
The design of Nail Intramedullari allows for minimal invasion. It enables faster recovery for patients compared to traditional methods. However, the technique is not without its challenges. Misalignment can occur during insertion. Moreover, complications such as infection can arise.
Despite these risks, Nail Intramedullari has transformed orthopedic practices. It combines innovative technology with essential surgical skills. Ultimately, its effectiveness is evident in improved patient outcomes. Understanding Nail Intramedullari's applications is vital for both healthcare providers and patients.
Definition and Overview of Nail Intramedullari
Nail intramedullari refers to a medical technique that uses a rod for stabilizing fractured bones. This method is especially useful for long bones, such as the femur or tibia. Surgeons insert a metal nail into the medullary canal of the bone. This provides internal fixation and aids in healing.
The procedure is minimally invasive. It often results in less soft tissue damage and quicker recovery for patients. However, it isn't always foolproof. Some patients may experience complications, such as infection or improper alignment. These issues can lead to prolonged rehabilitation.
Surgeons must assess each case individually. Understanding the anatomy and the extent of the fracture is vital. Despite its advantages, nail intramedullari requires careful consideration. It is important to weigh the benefits against potential risks. Each surgery can present unique challenges.
Historical Background of Intramedullary Nails in Surgery
The historical background of intramedullary nails reveals a fascinating evolution in surgical practices. Intramedullary nailing was developed to treat fractures effectively. Initially utilized in the early 20th century, these nails aimed to stabilize broken bones. Doctors faced numerous challenges in the early stages, such as infection and misalignment. They needed to find better solutions.
In the 1950s and 1960s, significant advancements took place. The intramedullary nail became popular due to its ability to provide strong support. Surgeons started using nails of various materials. With time, techniques improved. Yet, complications still arose. Understanding how to properly insert the nail was crucial. Not all cases resulted in ideal outcomes. Learning from failures has pushed innovations in design and application.
Another important aspect is interdisciplinary collaboration. Orthopedic surgeons worked closely with engineers. This partnership led to enhanced designs and materials. Modern intramedullary nails are more effective, yet some limitations remain. Surgeons continue to refine methods, ensuring better results. Exploring the history of these tools illustrates the ongoing journey of surgical excellence.
What is Nail Intramedullari and How is it Used in Surgery? - Historical Background of Intramedullary Nails in Surgery
| Year | Development | Key Innovator | Technique Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | Introduction of Intramedullary Nails | Alfredo A. Carpaneto | Provided preliminary techniques for stabilization of long bone fractures. |
| 1970 | Development of Reamed Intramedullary Nailing | G. M. Grosse | Enhanced fracture healing and reduced complications. |
| 1990 | Adoption of Locking Mechanism | Multiple Innovators | Improved stability for complex fractures and osteoporotic bone. |
| 2000 | Introduction of Biomechanical Studies | Research Teams | Focused on enhancing nail design for optimal performance. |
| 2020 | Use of 3D Printing for Custom Nails | Innovative Surgeons | Increased personalization for improved patient outcomes. |
Types of Intramedullary Nails Used in Orthopedic Procedures
Intramedullary nails are crucial in orthopedic surgery. These nails provide stability for broken bones, especially in the long bones. Surgeons rely on them for femoral and tibial fractures. Their design allows for less invasive procedures compared to other fixation methods. The placement of these nails occurs inside the medullary canal. This intramedullary placement minimizes surrounding tissue damage.
Different types of intramedullary nails exist, each tailored for specific fractures. The "locked" intramedullary nails are commonly used. They provide excellent rotational stability. However, they require precise insertion techniques. Some surgeons face challenges with alignment and locking mechanisms. Another option is the "un-locked" nails, which are easier to insert. They may not offer the same level of stability as locked nails, which might lead to complications in certain cases.
Surgeons also consider the patient's age and bone quality when selecting a nail type. Younger patients might heal faster, but older patients can pose problems due to poor bone density. Finding the best approach is a critical and sometimes difficult task. Surgeons continually reflect on their methods in hopes of improving outcomes. Understanding these details remains essential for effective treatment.
Surgical Procedure for Inserting Intramedullary Nails
Intramedullary nails are crucial in orthopedic surgery for stabilizing long bone fractures. Surgeons insert these nails within the bone's medullary cavity. This technique allows for a more stable and effective healing process. The insertion process involves careful assessment of the fracture type and location. The effectiveness rate for intramedullary nailing is reported to be between 90% and 95%, according to various studies.
The surgical procedure begins with a small incision at the fracture site. A guide wire is placed to direct the nail. This is followed by careful drilling to ensure proper alignment. X-rays are often used during the procedure to confirm placement. Anesthesia choice can also impact recovery time and patient comfort. Although this method shows promising results, some risks exist. Complications can include infection or nonunion of the fracture.
**Tips:** During recovery, patients should focus on rehabilitation. Engaging in prescribed physical therapy can aid the healing process. Listening to the healthcare provider is vital. Fracture healing varies; hence, patience is crucial. Regular follow-ups are important to monitor progress and adjust care plans accordingly.
Nail Intramedullari Usage in Surgery
Benefits and Risks Associated with Nail Intramedullari Surgery
Nail intramedullari is a surgical technique for bone stabilization. It involves inserting a metal rod into the marrow cavity of a bone. Surgeons often use it for fractures, especially in long bones like the femur or tibia. This method can lead to faster healing and recovery. It allows for early movement, which is crucial for maintaining muscle strength.
However, there are risks involved. Infection is a potential complication. Some patients may experience discomfort or pain after surgery. In rare cases, improper placement can occur, leading to further issues. One must consider the emotional impact as well. Facing surgery can be daunting, and recovery can test patience.
On the positive side, many patients find the procedure effective. The ability to resume normal activities sooner is often highlighted. Yet, not everyone has the same outcome. Some may feel frustrated if their recovery takes longer than expected. It's essential to weigh both benefits and risks before proceeding with this surgery.