Blog
How Solar Powered Street Lights are Transforming Urban Landscapes for a Sustainable Future
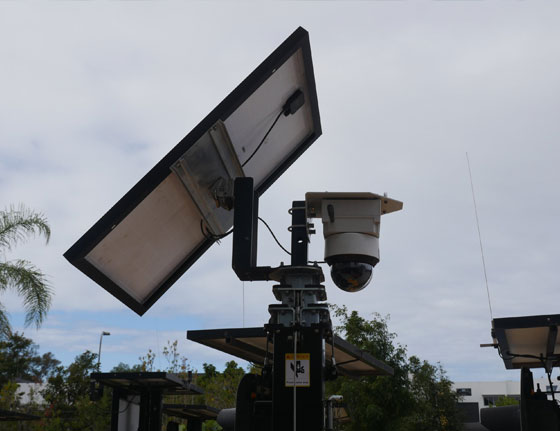
The increasing global emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency has catalyzed innovative solutions in urban infrastructure, notably the adoption of Solar Powered Street Lights. According to a recent report by the International Renewable Energy Agency, the global demand for solar lighting systems is projected to reach $19.5 billion by 2025, driven by advancements in solar technology and a growing awareness of environmental issues. These environmentally friendly lighting solutions not only reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also lead to substantial cost savings for municipalities, with estimates suggesting a 50% reduction in energy costs.

Furthermore, Solar Powered Street Lights contribute to enhanced public safety and urban aesthetics, creating well-lit spaces that deter crime and improve community engagement. This shift towards solar-powered solutions is reshaping urban landscapes, aligning with the broader goals of sustainable development and smarter cities throughout the world.
How to Select the Ideal Location for Solar Powered Street Lights in Urban Areas
Selecting the ideal location for solar powered street lights in urban areas is crucial to maximize their benefits while ensuring safety and efficiency. A key factor to consider is the accessibility of direct sunlight. Placing lights in open areas free from tall buildings or trees guarantees optimal solar panel performance, allowing the lights to recharge fully during the day. Urban planners should conduct a thorough assessment of the site's sun exposure throughout different times of the year to avoid shadows that can inhibit solar energy absorption.
Additionally, the location should prioritize high foot traffic and communal spaces to enhance safety and visibility. Areas near parks, pathways, and public transport stations are excellent candidates as they not only illuminate these spaces but also promote their usage during nighttime. Involving community feedback can also play a significant role in selecting locations, as residents can provide insights on areas that require better lighting for safety and mobility. By carefully considering these factors, cities can effectively implement solar powered street lights, contributing to a more sustainable and enhanced urban environment.

How to Assess the Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings of Solar Street Lighting
The assessment of energy efficiency and cost savings in solar street lighting represents a significant step towards sustainable urban development. By leveraging solar technology, municipalities not only reduce their reliance on conventional electricity sources but also lower long-term operational costs. In Mexico, the Energy Efficiency in Public Facilities (PRESEMEH) project demonstrated the effectiveness of this approach, enhancing energy sustainability in public facilities, including hospitals. The integration of solar street lights in urban landscapes creates safer environments while contributing to significant savings on electricity bills.
As the global solar street lighting market is expected to grow from USD 2.38 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 7.80 billion by 2034, cities are increasingly recognizing the importance of these systems. Projects in Australia forecast a market size of USD 757.08 million by 2033, underscoring the rising demand for renewable energy solutions in urban planning. This shift not only supports energy efficiency initiatives but also encourages investments in fleet and renewable energy projects, paving the way for a more sustainable future in urban infrastructure.

How to Integrate Smart Technology with Solar Street Lights for Enhanced Urban Safety
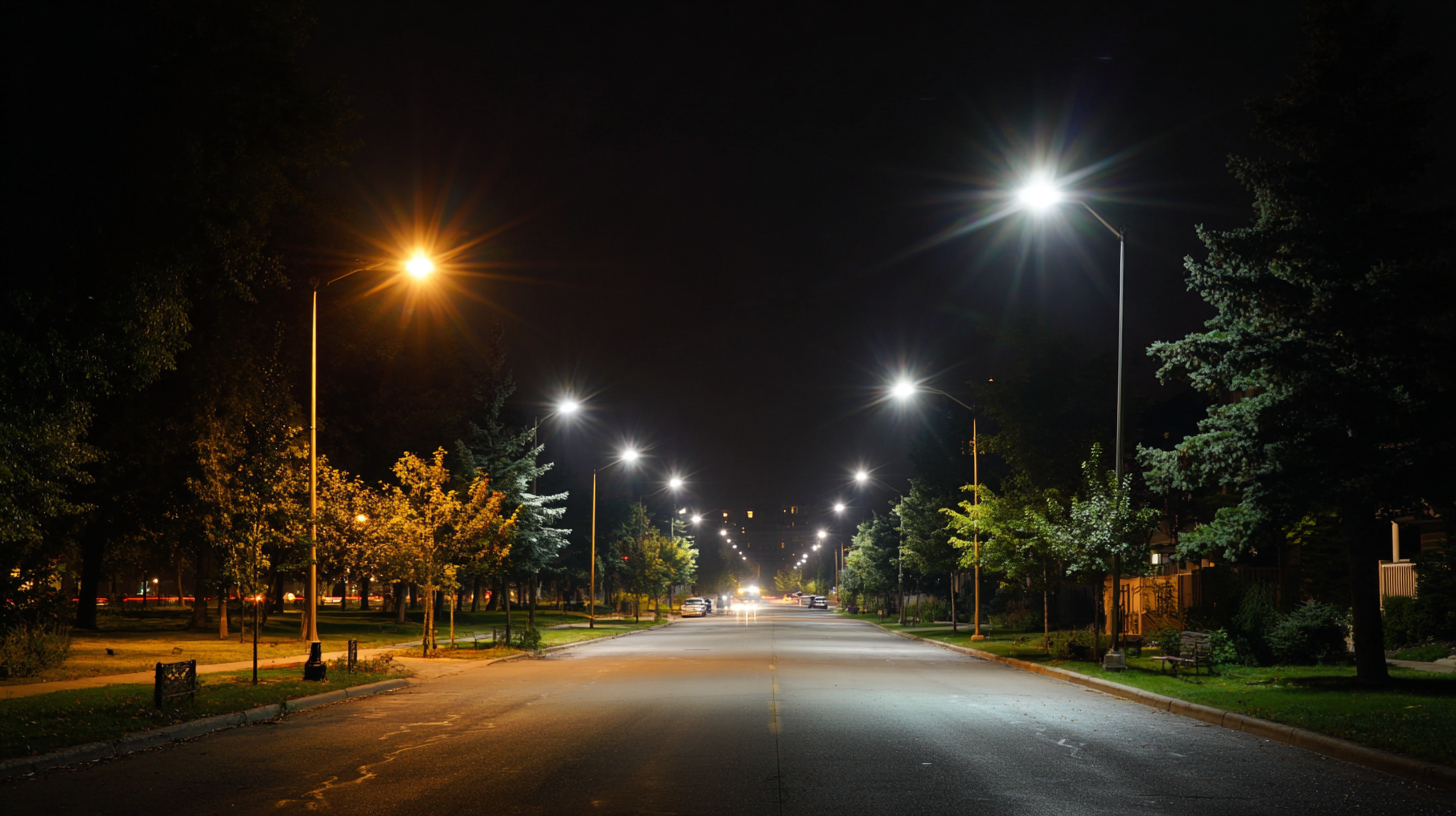
The integration of smart technology with solar-powered street lights is revolutionizing urban safety, creating environments that are not only eco-friendly but also secure. By equipping these lights with sensors, cameras, and communication tools, cities can monitor real-time conditions and enhance safety measures. For example, motion detectors can trigger increased brightness in lights when movement is detected, ensuring better visibility in dim areas. This proactive approach deters crime and helps ensure that public spaces are well-lit and inviting.
Moreover, smart solar street lights can connect to an urban network, allowing for data sharing and analysis. This data can provide insights into traffic patterns, pedestrian activity, and even environmental conditions. Cities can utilize this information for better urban planning and resource allocation. Additionally, integrated features like emergency alarms and automated alerts can quickly notify authorities of incidents, thus reducing response times and enhancing overall community safety. Such innovations not only promote a sustainable approach to urban illumination but also reinforce the commitment to providing safer urban environments for residents and visitors alike.
How to Engage the Community in the Adoption of Solar Powered Street Lighting
Communities around the world are recognizing the importance of adopting solar-powered street lighting to promote sustainability and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Engaging local residents in the decision-making process is crucial for the successful implementation of these initiatives. According to a recent report, the Africa off-grid solar lighting market is projected to grow significantly, reaching USD 1.372 billion by 2033. This growth indicates a rising awareness and willingness among communities to invest in renewable energy solutions that not only light up public spaces but also contribute to environmental conservation.
Effective community engagement strategies include organizing informational workshops and inviting residents to participate in planning sessions. A study highlights that community projects can serve as a vital bridge between local needs and sustainable solutions, fostering collaboration among residents. The Welsh Government, for example, has set ambitious targets for generating locally-owned renewable energy, emphasizing that the involvement of community members is essential for achieving these goals. By empowering citizens to lead the transition toward solar-powered street lighting, communities can enhance both their energy resilience and their commitment to a sustainable future.
Community Engagement in the Adoption of Solar Powered Street Lighting
How to Overcome Common Challenges in Implementing Solar Street Lighting Solutions
Implementing solar street lighting solutions presents several common challenges, but these can be effectively managed with strategic planning. One primary obstacle is the initial investment cost, which can be high for many municipalities. To overcome this, cities can explore public-private partnerships or seek funding from government grants specifically designed for renewable energy projects. Engaging local communities in the funding process not only helps finance the installation but also encourages public support and acceptance of solar technology.
Another challenge is ensuring the reliability and performance of solar street lights, particularly in areas with inconsistent sunlight. This can be mitigated by adopting advanced technology such as solar panels with higher efficiency rates and integrating battery storage systems that can store surplus energy for use during cloudy days or at night. Regular maintenance and timely upgrades are also essential to ensure that the lights operate at optimal performance and continue to meet urban lighting needs effectively, fostering a safer and more sustainable urban environment.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Innovative Alternatives to Solar Street Lights for Sustainable Urban Lighting Solutions
-

Unlocking the Advantages of High Efficiency Solar Street Lights with Pole for Global Buyers
-

Revolutionizing Urban Lighting with Eco Friendly Solar Street Lights
-

The Comprehensive Guide to Sourcing the Best Solar Street Lights With Pole for Sustainable Urban Development
-

Navigating Import Export Certifications for Best Solar Powered Street Lights for Global Buyers
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Best Solar Panel for Outdoor Lights